CNC turning parts are among the most widely used components in modern manufacturing. From automotive assemblies and industrial machinery to medical devices and aerospace systems, countless products rely on precisely machined rotational parts to function reliably.

If you are researching CNC turning parts, you may be asking very practical questions:
- What exactly are CNC turning parts?
- What kinds of parts can be made using CNC turning?
- How accurate are CNC precision turned parts?
- When is CNC turning a better choice than CNC milling?
- How do buyers evaluate a reliable CNC turned parts manufacturer?
This article answers those questions clearly and objectively.
It is written to help engineers, buyers, and sourcing professionals understand CNC turning parts at a foundational level—before moving on to supplier selection or cost evaluation.
What Are CNC Turning Parts?
CNC turning parts are components produced through a machining process in which a workpiece rotates while a cutting tool removes material to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. This process is performed on a CNC lathe or CNC turning center, where movements are controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) programs.
Unlike CNC milling—where a rotating tool cuts a stationary workpiece—CNC turning relies on rotational symmetry. Because of this, CNC turning parts are typically round or cylindrical, although modern machines can also produce flats, slots, holes, and other secondary features.
Key Characteristics of CNC Turning Parts
CNC turning parts are known for several defining characteristics:
- Rotational geometry: Most CNC turned parts have circular cross-sections.
- High dimensional accuracy: Tight tolerances can be maintained consistently.
- Excellent surface finish: Continuous cutting produces smooth surfaces.
- Repeatability: CNC control ensures consistency from part to part.
- Production efficiency: Especially suitable for medium- to high-volume runs.
These characteristics make CNC turning parts ideal for applications where concentricity, roundness, and surface quality are critical.
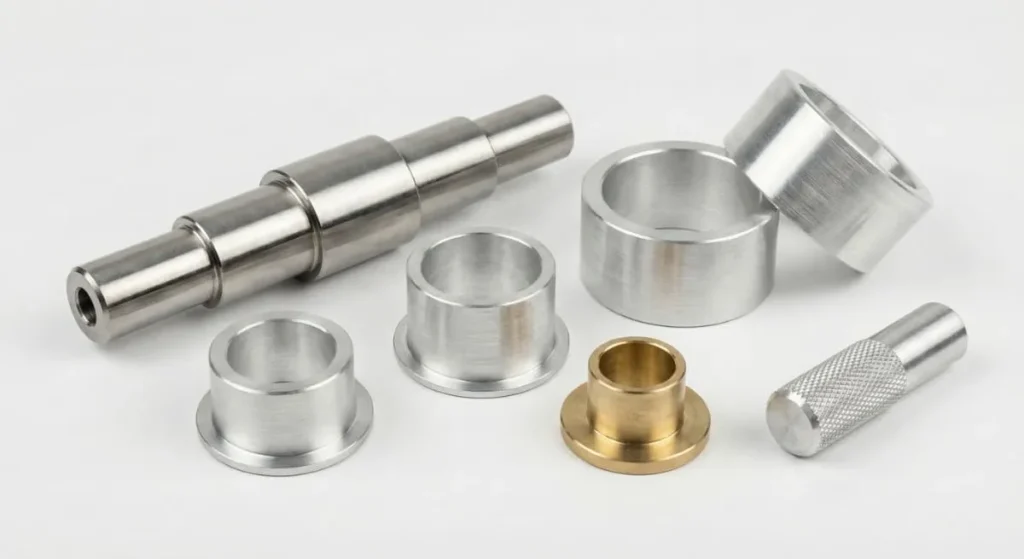
Typical CNC Turning Parts (With Examples)
One of the most common questions buyers ask is: What parts can CNC turning actually make?
Below are some of the most common CNC turning parts used across industries.
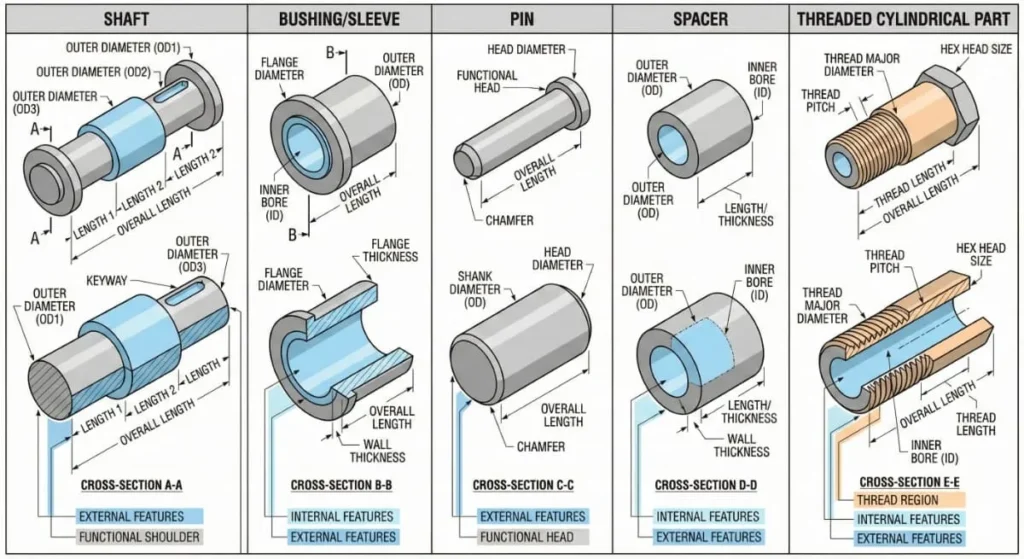
Shafts
Shafts are classic CNC turning parts. They are used to transmit motion or torque in mechanical systems.
Common applications include:
- Automotive drive shafts
- Motor shafts
- Transmission components
- Industrial machinery spindles
CNC turning allows precise control of diameter, straightness, and concentricity—critical for rotating shafts.
Bushings and Sleeves
Bushings and sleeves are cylindrical components used to reduce friction, support shafts, or act as wear surfaces.
Typical uses:
- Suspension systems
- Industrial equipment
- Hydraulic systems
Many CNC turned parts manufacturers produce bushings in brass, bronze, steel, or engineering plastics depending on load and wear requirements.
Pins and Dowels
Pins are small but essential CNC turning parts used for alignment, positioning, or fastening.
Examples include:
- Locating pins
- Hinge pins
- Precision dowel pins
Because these parts often require tight diameter tolerances, CNC precision turned parts are preferred over manual machining.
Spacers
Spacers maintain consistent distances between components in assemblies.
They are commonly used in:
- Automotive assemblies
- Electronics housings
- Industrial frames
CNC turning ensures accurate length and parallel faces, even in high volumes.
Threaded Parts
Threaded CNC turning parts include:
- Threaded rods
- Studs
- Fittings
- Connectors
Threads can be cut or rolled on CNC lathes with high repeatability, ensuring proper fit and function in mating assemblies.
Nozzles and Fittings
Fluid-handling systems often rely on CNC turned parts such as:
- Fuel nozzles
- Hydraulic fittings
- Pneumatic connectors
These parts frequently require smooth internal bores and precise geometry, making CNC turning an ideal process.
Materials Commonly Used for CNC Turning Parts
CNC turning parts can be produced from a wide range of materials. Material selection affects performance, machinability, cost, and lead time.
Metal Materials
Aluminum
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to machine. Aluminum CNC turning parts are widely used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics applications.
Stainless Steel
Offers strength and corrosion resistance. Common grades include 303, 304, and 316. Stainless steel CNC turned parts are often used in medical, food-grade, and outdoor environments.
Carbon Steel
Cost-effective and strong. Carbon steel CNC turning parts are commonly used in industrial machinery and structural components.
Brass and Copper Alloys
Excellent machinability and electrical conductivity. Brass CNC turned parts are often used in fittings, valves, and electrical components.
Plastic Materials
CNC turning is not limited to metal. Many CNC turned parts manufacturers also machine plastics such as:
- POM (Delrin)
- Nylon
- PTFE
- PEEK
Plastic CNC turning parts are used for insulation, chemical resistance, and lightweight applications.
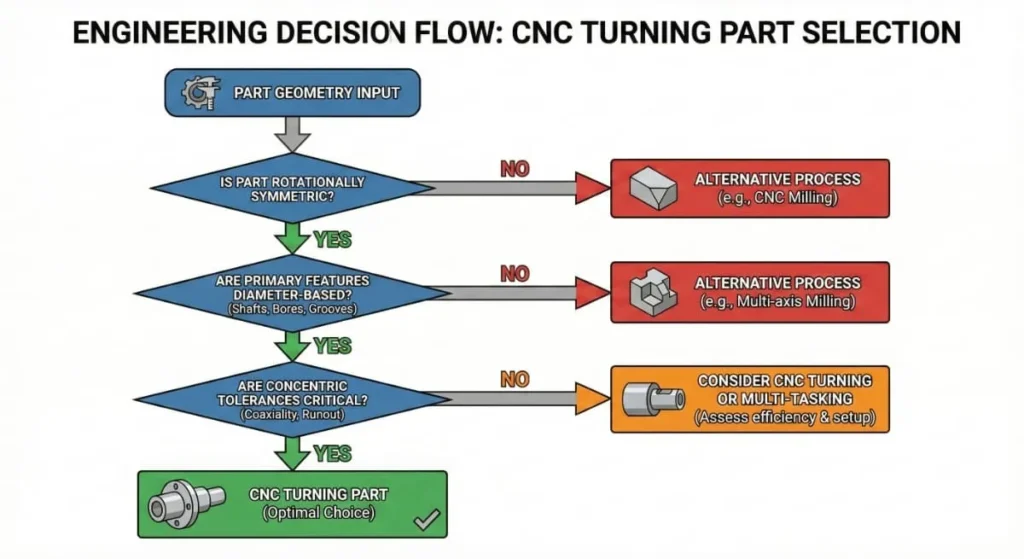
CNC Turning vs CNC Milling: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the difference between CNC turning and CNC milling helps buyers choose the right process.
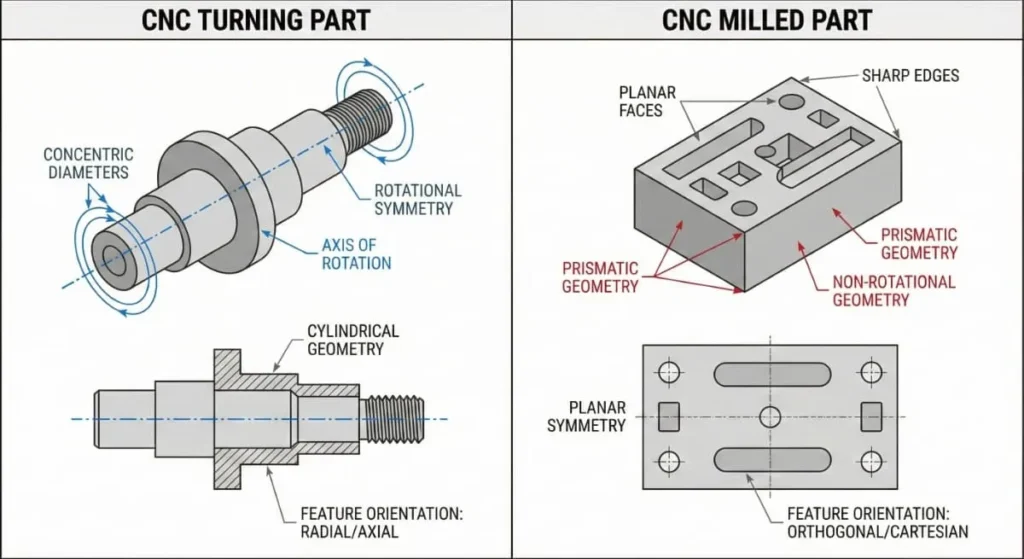
| Feature | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Workpiece motion | Rotates | Stationary |
| Tool motion | Linear | Rotating |
| Best for | Cylindrical parts | Prismatic or complex shapes |
| Efficiency | High for round parts | Lower for rotational parts |
| Typical parts | Shafts, bushings, pins | Plates, housings, brackets |
Rule of thumb:
If a part is primarily round or axis-symmetric, CNC turning parts are usually more accurate and cost-effective than milled parts.
CNC Turning Process: How CNC Turning Parts Are Made
Understanding the process behind CNC turning parts helps buyers evaluate supplier capabilities.
Step 1: Material Preparation
Raw material is typically supplied as bar stock or rod stock. The diameter is selected to minimize waste and machining time.
Step 2: CNC Programming
Engineers program the turning operations using CAM software. Proper programming is essential for:
- Dimensional accuracy
- Tool life
- Surface finish
- Cycle time optimization
Experienced CNC turned parts manufacturers invest heavily in skilled programmers.
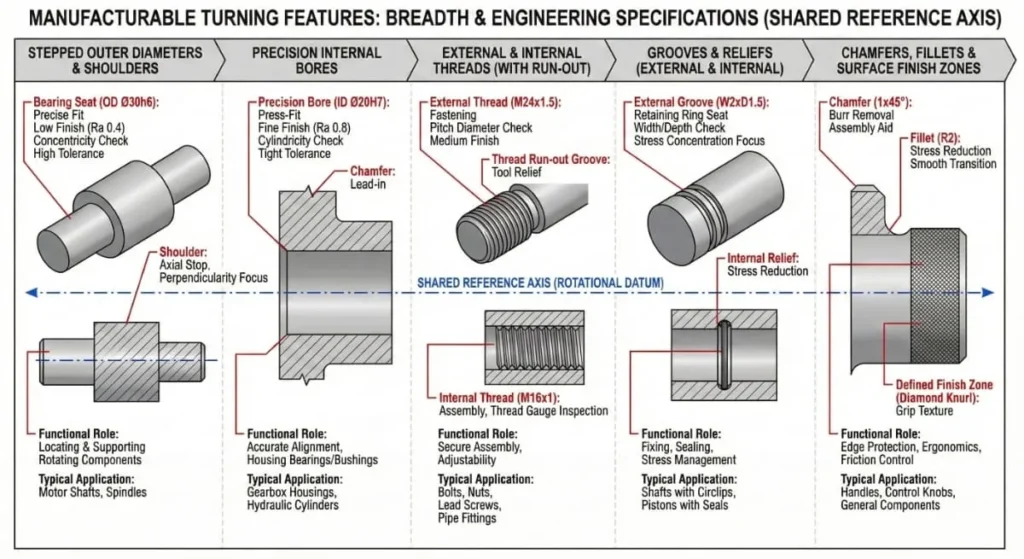
Step 3: Turning Operations
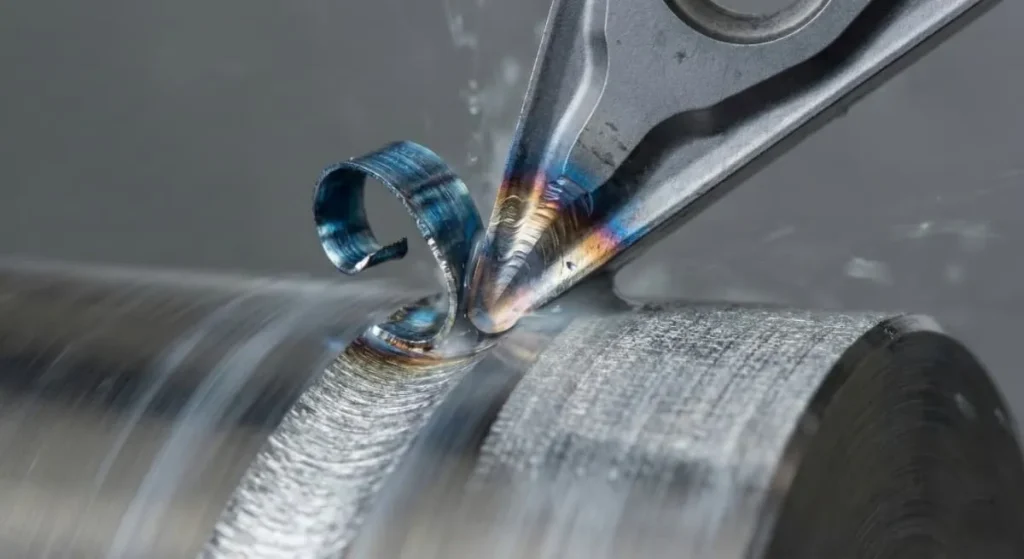

Common CNC turning operations include:
- Facing
- Outside diameter (OD) turning
- Inside diameter (ID) boring
- Grooving
- Threading
- Parting-off
Advanced machines can complete multiple operations in a single setup, reducing errors.
Step 4: Secondary Operations (If Required)
Some CNC turning parts require additional features such as:
- Cross-drilled holes
- Milled flats
- Knurling
Modern CNC turning centers with live tooling can perform these operations without removing the part.
Step 5: Inspection and Quality Control
Professional CNC precision turned parts are inspected using:
- Micrometers and calipers
- Bore gauges
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines)
Inspection ensures that parts meet drawing requirements before shipment.
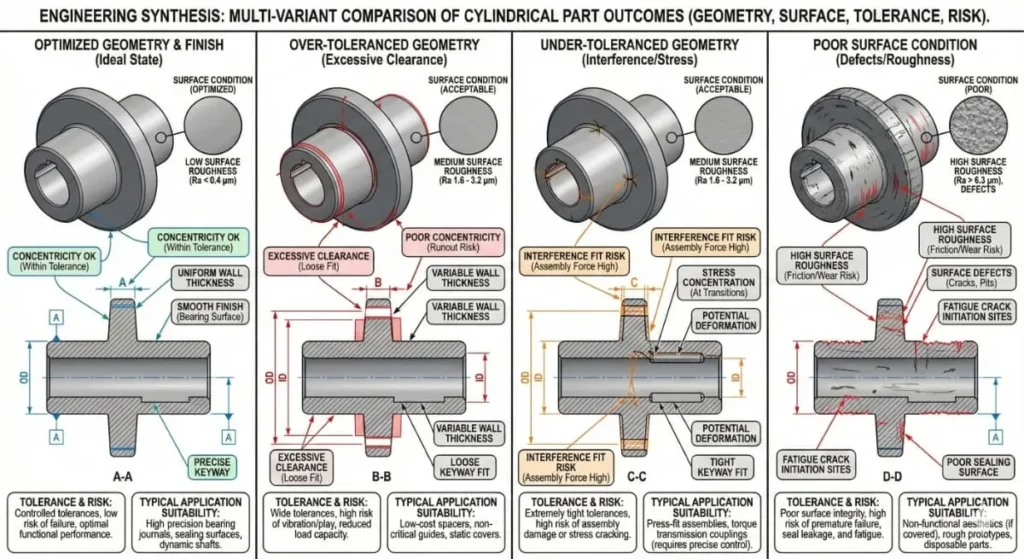
Tolerances for CNC Precision Turned Parts
One of the key advantages of CNC turning parts is accuracy.
Typical tolerances include:
- ±0.01 mm for standard CNC turning parts
- ±0.005 mm or better for CNC precision turned parts
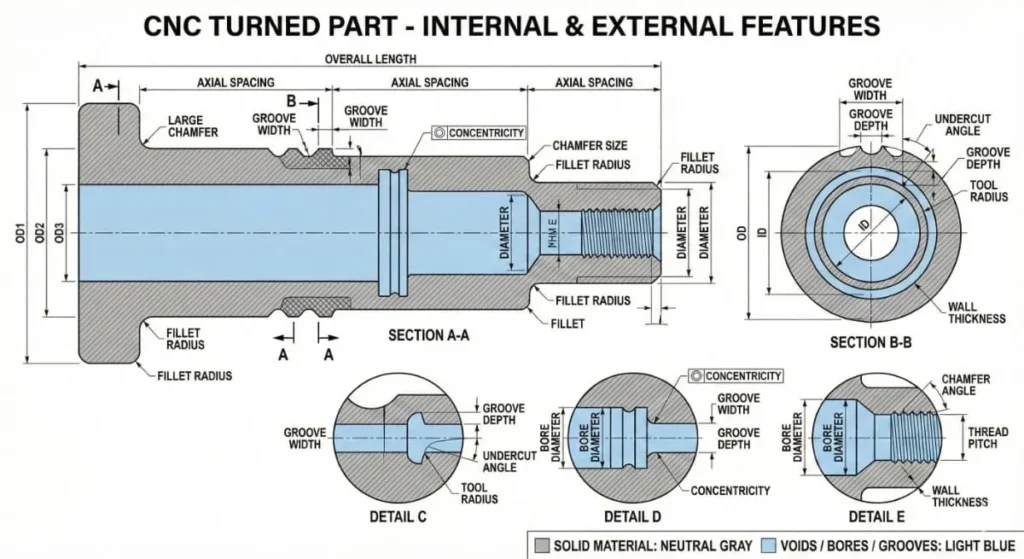
Achievable tolerances depend on:
- Material type
- Part geometry
- Machine capability
- Process stability
A reliable CNC turned parts manufacturer will review tolerances during the quoting stage to confirm feasibility.
Surface Finish Options for CNC Turning Parts
Surface finish affects function, wear, and appearance.
Common finishes for CNC turning parts include:
- As-machined
- Polished
- Bead blasted
- Anodized (aluminum)
- Zinc plated or black oxide (steel)
- Passivated (stainless steel)
Surface roughness is typically specified as Ra (µm) on engineering drawings.

Industries That Use CNC Turning Parts
CNC turning parts are used across many industries:
- Automotive: shafts, spacers, fittings, engine components
- Aerospace: precision shafts, connectors, bushings
- Medical: implants, surgical instruments, housings
- Industrial equipment: couplings, rollers, pins
- Energy: valves, connectors, pump components
Each industry may require different documentation, traceability, or inspection standards.
How to Choose a Reliable CNC Turned Parts Manufacturer
Selecting the right CNC turned parts manufacturer is critical for quality and long-term reliability.
Key evaluation factors include:
- Experience with custom CNC turning parts
- Ability to hold required tolerances
- Quality management systems (such as ISO 9001)
- Clear technical communication
- Willingness to provide DFM feedback
Buyers often search locally for suppliers, using terms such as cnc turned parts manufacturer georgia, to reduce lead time and simplify communication. Local sourcing can offer advantages, but global suppliers with strong engineering teams and quality systems can also be highly competitive.
Local vs Global CNC Turned Parts Manufacturing
When sourcing CNC turning parts, buyers typically consider both local and overseas manufacturers.
Local manufacturers may offer:
- Easier audits
- Faster initial communication
- Shorter shipping times
Global manufacturers may offer:
- Greater production capacity
- Competitive pricing
- Specialized CNC turning expertise
The best choice depends on project requirements, volume, and quality expectations.
Common Mistakes When Sourcing CNC Turning Parts
Understanding common pitfalls helps buyers avoid costly delays.
Mistake 1: Over-specifying tolerances
Unnecessarily tight tolerances increase cost without improving function.
Mistake 2: Ignoring DFM feedback
Designs that are difficult to machine lead to higher scrap rates.
Mistake 3: Choosing suppliers based only on price
Inconsistent quality often results in higher long-term costs.
A professional CNC turned parts manufacturer will help identify and prevent these issues early.
FAQ: CNC Turning Parts
What are CNC turning parts used for?
CNC turning parts are used in applications requiring precise round or cylindrical components, such as shafts, bushings, and fittings.
How accurate are CNC precision turned parts?
High-quality CNC precision turned parts can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, depending on material and design.
Are CNC turned parts suitable for high-volume production?
Yes. CNC turning is highly efficient for medium- and high-volume production of rotational parts.
What is the difference between CNC turned parts and machined parts?
CNC turned parts are a subset of machined parts, specifically produced using turning processes on lathes.
Conclusion: Understanding CNC Turning Parts
CNC turning parts play a fundamental role in modern manufacturing. Their accuracy, efficiency, and versatility make them indispensable across industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to medical and industrial equipment.
By understanding:
- What CNC turning parts are
- What types of parts can be produced
- Which materials and tolerances are realistic
- How to evaluate a CNC turned parts manufacturer
buyers and engineers can make more informed sourcing decisions and reduce manufacturing risk.
If you are moving beyond basic research and beginning to source custom CNC turning parts or CNC precision turned parts, working with an experienced manufacturer that understands both engineering and production requirements is essential.
Next step:
If you are evaluating suppliers or preparing drawings for quotation, welcome to contact CNMP Team.

