Introduction: Why Precision is More Than Just a Number
In the world of modern manufacturing, cnc precision machining parts are the backbone of innovation. Whether you are designing aerospace components, medical devices, or custom automotive assemblies, the difference between success and failure often comes down to microns .
But for procurement managers and engineers sourcing from overseas, the challenge isn’t just about finding a shop that owns a CNC machine. It is about finding a partner who understands that “precision” isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a strict adherence to tolerance, surface finish, and material integrity .
Are you tired of receiving parts that don’t fit? Or struggling with suppliers who nod “yes” to every request but fail to deliver on complex geometries? . If you have faced common pain points like parts that look fine visually but fail during assembly, or tolerances that drift between batches, this guide is for you .
This comprehensive article serves as the ultimate resource for B2B professionals. We will break down everything you need to know about precision cnc machining services: from mastering Design for Manufacturing (DFM) strategies that can cut your costs by up to 30%, to implementing a remote quality control protocol that ensures you never receive a bad batch again .
Part 1: What Exactly Are CNC Precision Machining Parts?
At its core, precision cnc machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where computer software (CAD/CAM) controls machine tools to remove material from a solid block . However, simply removing material is not enough to qualify as “precision.”
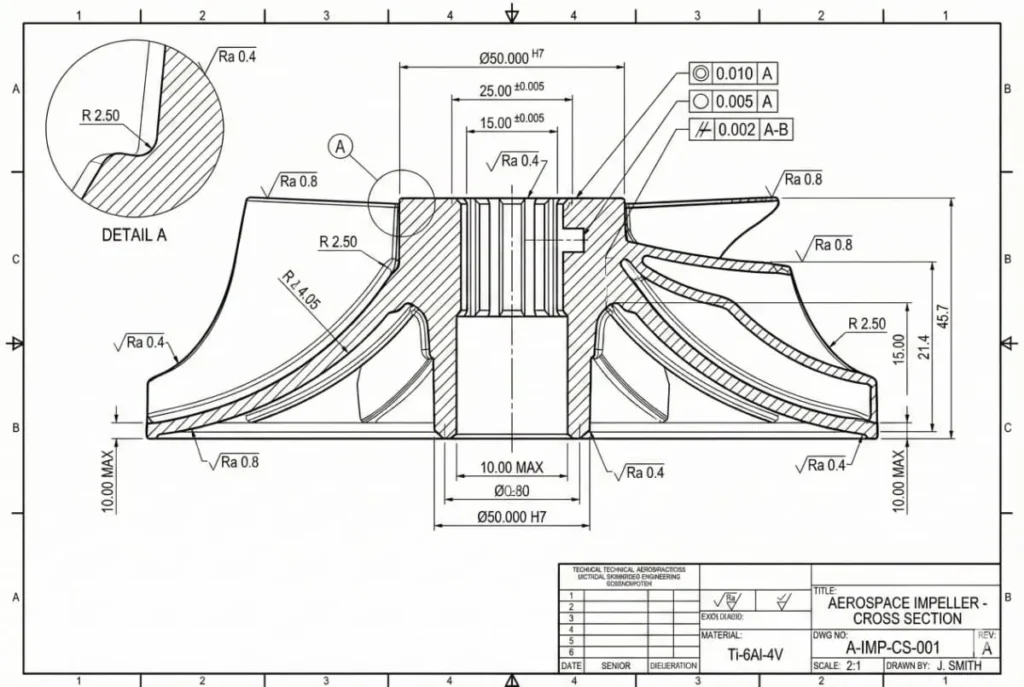
When we discuss cnc precision machining parts, we are strictly referring to components that meet high-tier criteria for accuracy and repeatability . These are not general hardware store brackets; these are engineered components used in high-stakes industries like aerospace, medical devices, and industrial automation .
Precision CNC Machining vs. Conventional Machining
To help you understand the value proposition, here is a direct comparison of capabilities. This data is critical for determining if your project actually requires precision services.
| Feature | Precision CNC Machining | Conventional Machining |
| Tolerance Capability | ±0.005mm – ±0.02mm | ±0.1mm (Typical) |
| Repeatability | Excellent (Computer Controlled) | Operator-Dependent |
| Geometry | Complex, Multi-axis (4-5 Axis) | Limited to Simple Shapes |
| Documentation | Full Traceability (CMM, COA) | Limited |
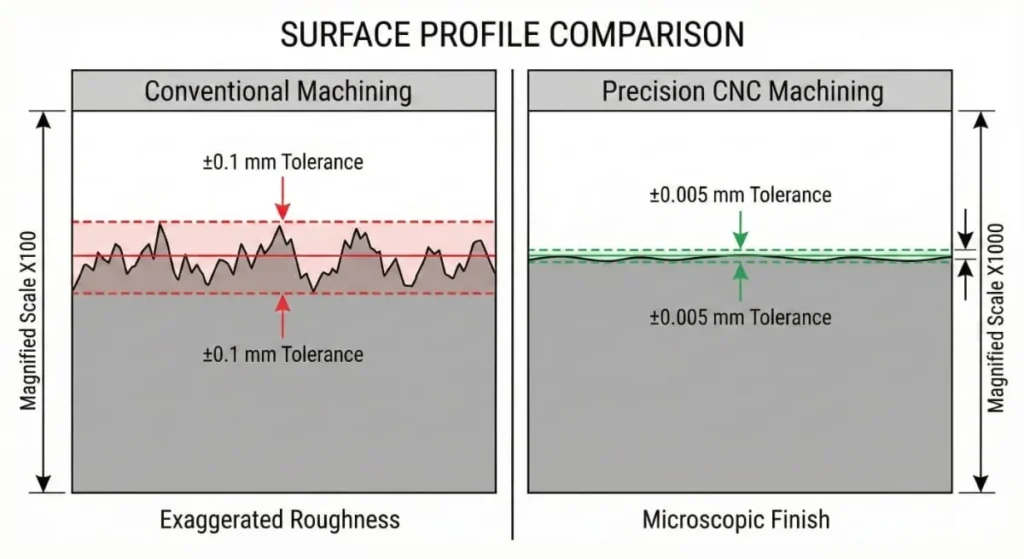
Expert Note: Precision isn’t just about the machine. A high-end 5-axis machine operated by an inexperienced technician will still produce scrap. True precision comes from thermal stability, tool wear management, and the skill of the programmer .
Part 2: Core Processes – How We Create Precision
To create cnc precision machined parts, manufacturers utilize various specialized processes. Understanding the difference between these methods helps you design better parts and select the right service .
1. CNC Milling Services (3-Axis, 4-Axis, & 5-Axis)
Milling is the most common method for prismatic parts. The workpiece remains stationary (mostly) while the cutting tool rotates .
- 3-Axis Milling: Best for simple flat surfaces and holes. It is cost-effective but requires manual repositioning for multiple sides .
- 5-Axis CNC Machining: The table and tool move on 5 axes simultaneously . This is critical for complex cnc precision machining parts like turbine blades or aerospace impellers .
- Why it matters: It reduces setup time and improves accuracy because the part doesn’t need to be moved manually between operations, reducing tolerance stack-up .
2. CNC Turning (Lathe) Services
Used for cylindrical parts like shafts, pins, and spacers. In this process, the part rotates while the tool moves linearly .
- Swiss-Style Turning: A specialized form of turning for very small, long, and slender parts (often used in medical devices). It offers superior support to the material, preventing deflection during cutting . This ensures excellent concentricity and roundness .
3. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
Sometimes, the geometry is too complex for a spinning cutter (e.g., sharp internal corners). We use Wire EDM or Sinker EDM to burn away material using electrical sparks . This is essential for hardened steels and mold making .
Part 3: Material Selection for High-Accuracy Components
The material you choose dictates the machining strategy, cost, and final performance of your cnc precision machining parts .
Metal Alloys
- Aluminum (6061, 7075): The king of prototyping and aerospace. It machines fast and holds tolerances well. AL7075 is preferred for high-stress applications .
- Stainless Steel (304, 316, 17-4PH): Notorious for work-hardening. It requires rigid setups and premium cooling strategies to maintain precision .
- Selection Tip: Choose 316 for superior corrosion resistance in marine or medical use .
- Titanium (Grade 5): Offers a high strength-to-weight ratio but is difficult to machine due to heat generation .
- Brass & Copper: Excellent for electrical contacts and low-friction applications .
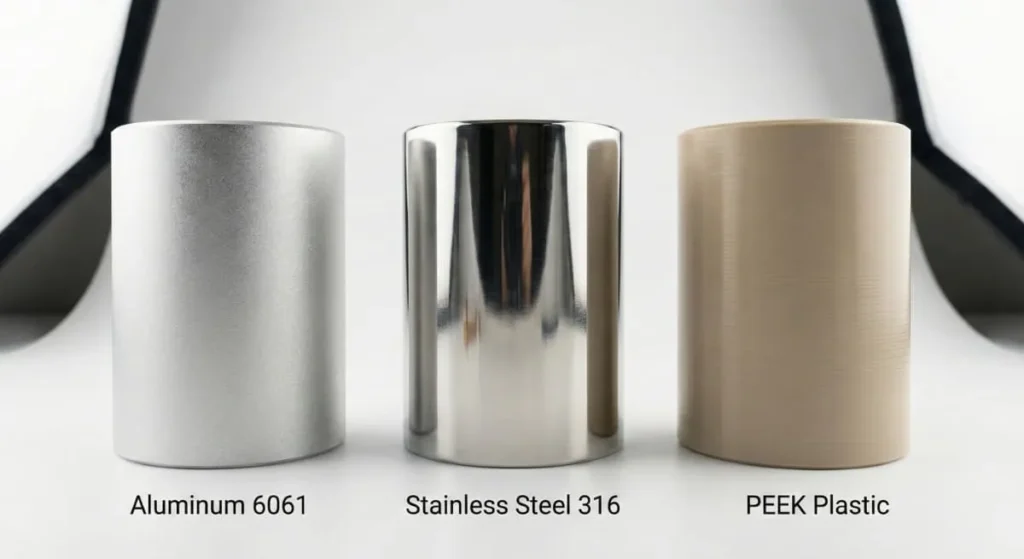

Engineering Plastics
- PEEK: A high-performance plastic used in medical implants. It is stable and capable of holding very tight metal-like tolerances .
- Delrin (POM): The easiest plastic to machine; great for gears and sliding mechanisms .
Part 4: The “Hidden” Cost of Precision – Smart Tolerancing Strategy
(Gap Analysis Strategy: Addressing Cost Optimization)
One of the biggest mistakes we see in drawings from overseas clients is “blanket tolerancing” . This occurs when an engineer applies a strict tolerance (e.g., +/- 0.005mm) to every dimension on the drawing, even non-critical ones .
The Cost Implications
Why is this a problem? Achieving +/- 0.005mm requires:
- Slower feed rates (more machine time) .
- More frequent tool changes (higher tooling cost) .
- 100% inspection rates (higher QC labor) .
- Ultimately, tightening a tolerance from ±0.02 mm to ±0.01 mm can increase cost by 20–40% .
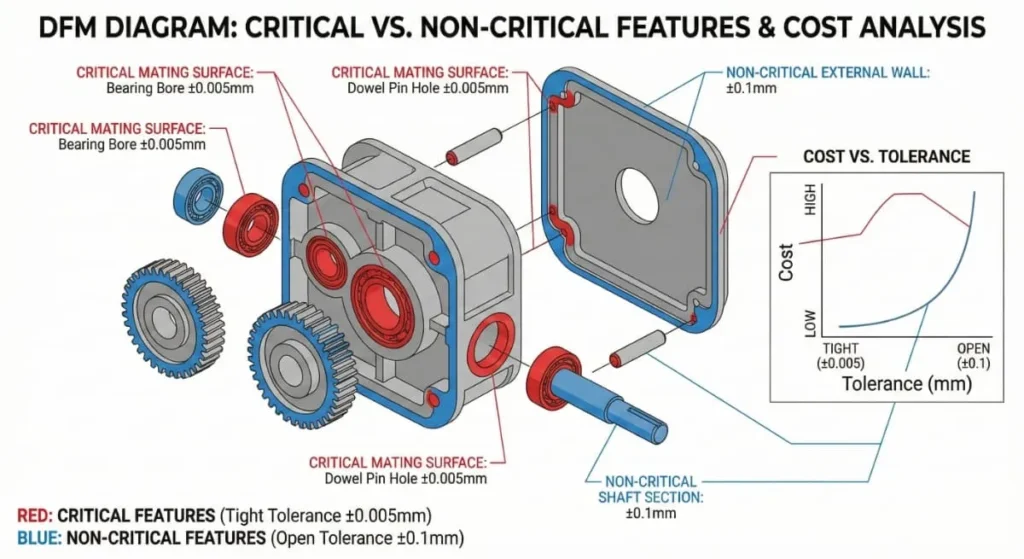
The Solution: GD&T Optimization
To optimize the cost of your precision cnc machining parts, you should adopt a “Smart Tolerancing” approach:
- Critical Features Only: Only apply tight tolerances to mating surfaces (bearing fits, sliding faces) .
- Open Up the Rest: For external aesthetic walls or non-mating surfaces, standard ISO 2768-m (medium) tolerances are usually sufficient .
- Use GD&T: Instead of tight linear tolerances, use Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (e.g., Position, Concentricity) to describe intent . This gives the machinist “wiggle room” while ensuring the part fits perfectly .
Part 5: Remote Quality Control – How We Verify Your Parts
(Gap Analysis Strategy: Addressing Trust & E-A-T)
When you are ordering precision cnc machining services from overseas, you can’t walk onto the factory floor to check the parts yourself. You need a proxy . A professional manufacturing partner provides transparency through documentation.
The Verification Protocol
Here is the standard you should demand from any supplier:
- Material Certification (COA): Proof that the aluminum used is actually 6061-T6, traceable to the mill .
- FAI (First Article Inspection): A detailed report checking the first part off the line against every dimension on your drawing .
- CMM Reports: For complex cnc precision machining parts, calipers are not enough. A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) probes the part in 3D space to verify complex geometries .
- Photos & Video: We provide high-resolution photos of the parts next to measuring tools before crating .
Our Promise: We don’t just ship parts; we ship confidence. Every batch goes through a rigorous visual and dimensional check before it leaves our facility .
Part 6: Case Study – Automotive Custom Wheel Hubs
To illustrate our expertise in action, let’s look at a real-world example of precision cnc machining.
The Client: A US-based automotive client requiring custom 6061-T6 wheel hubs .
The Challenge: The center bore tolerance was extremely tight (H7 fit) to prevent vibration at high speeds. This is a critical safety feature . Standard turning might leave slight variations that could lead to assembly failure.
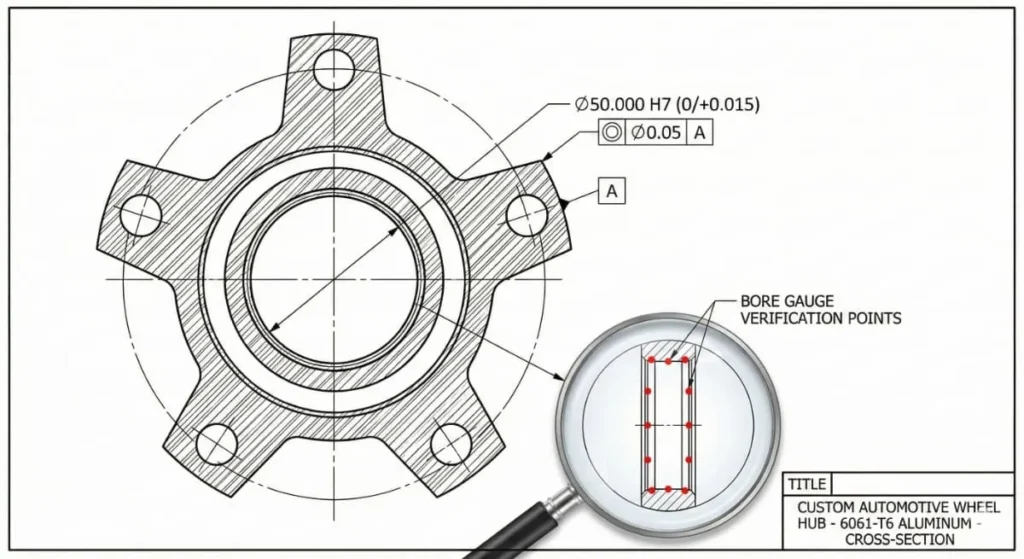
The Solution:
- We utilized our CNC turning service for the initial profile.
- Followed by a 4-axis mill for the complex bolt patterns .
- Critical Step: We used a bore gauge to verify the center hole on 100% of the parts, rather than just a random sampling .
The Result: Zero defects and a recurring monthly order. This case highlights why specific inspection protocols are vital for cnc precision machining parts .
Part 7: Buyer’s Guide – How to Choose the Right Supplier
Sourcing cnc precision machining parts is not a commodity transaction; it is a partnership. Use this checklist to evaluate potential suppliers :
- Proven Experience: Do they have case studies for parts similar to yours?
- Clear Tolerance Capability: Can they articulate the difference between +/- 0.01mm and +/- 0.1mm?
- Transparent Communication: Do they offer DFM feedback to lower your costs?
- Quality Documentation: Do they offer CMM reports and Material Certifications (COA)?
- Engineering Support: Can they handle high-mix, low-volume orders and prototypes?
FAQ: Common Questions About CNC Precision Machining
Q1: What is the standard lead time for precision cnc machining parts?
Typically, prototyping takes 3-7 days, while low-volume production (100-500 parts) takes 2-3 weeks . This depends heavily on material availability and surface finishing requirements .
Q2: What tolerance can CNC precision machining achieve?
Typically ±0.01 mm is standard for precision work. Tighter tolerances (down to ±0.005mm) are possible but will come with additional cost and inspection time .
Q3: How do you ensure the confidentiality of my design?
We sign a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) with all clients before receiving data. Your IP is safe with us .
Q4: What file formats do you accept for quotes?
For the most accurate quote, please provide a 3D CAD file (STEP or IGS) and a 2D PDF drawing. The 3D file is used for CAM programming, while the 2D drawing specifies tolerances, threads, and finishes .
Q5: What is the difference between CNC Machining and 3D Printing?
CNC is subtractive (cutting away), offering superior strength, surface finish, and material options (metals). 3D printing is additive, great for complex internal geometries but generally weaker and less precise than precision cnc machining parts .
Conclusion & Call to Action
Sourcing cnc precision machining parts doesn’t have to be a gamble . By understanding the capabilities of milling and turning, selecting the right materials, and partnering with a supplier who prioritizes communication and quality control, you can streamline your supply chain and reduce costs .
Whether you need a single prototype to validate a design or a batch of 500 complex components for a product launch, reliable manufacturing is within reach .
Ready to get started?
Don’t let poor quality hold your project back.
Upload Your Drawings Here for a free DFM review and quotation within 24 hours. Let’s build something precise, together .

