Introduction
When it comes to the aviation and defense industries, “good enough” is simply not an option. A single component failure can have catastrophic consequences, which is why the demand for cnc machining aerospace parts is driven by an unyielding need for precision, traceability, and material integrity.
For procurement managers and engineers sourcing from overseas, finding a partner capable of meeting these stringent requirements is often a challenge. You may have dealt with suppliers who promised tight tolerances but delivered out-of-spec components, or perhaps you struggled with communication barriers that delayed your supply chain.
This guide is designed to cut through the noise. We will explore the technical intricacies of aerospace parts cnc machining manufacturing, from the exotic materials used to the rigorous quality control protocols required. Whether you are designing turbine blades or structural airframe components, understanding these factors is essential to selecting a manufacturing partner who can deliver on time and to specification.
3. The Critical Role of CNC Machining in Aerospace
Why Precision is Non-Negotiable
The aerospace sector operates under extreme conditions. CNC machining aerospace parts are subjected to immense pressure, drastic temperature fluctuations, and high-speed vibrations. Consequently, cnc machining aerospace parts requires tolerances that frequently hit +/- 0.005mm or tighter.
Unlike standard commercial machining, aerospace manufacturing demands:
- Weight Reduction: Removing maximum material without compromising structural integrity (lightweighting).
- Complex Geometries: Creating aerodynamic shapes that require multi-axis machining.
- Zero Defect Mentality: Strict adherence to DFM (Design for Manufacturing) and quality assurance.
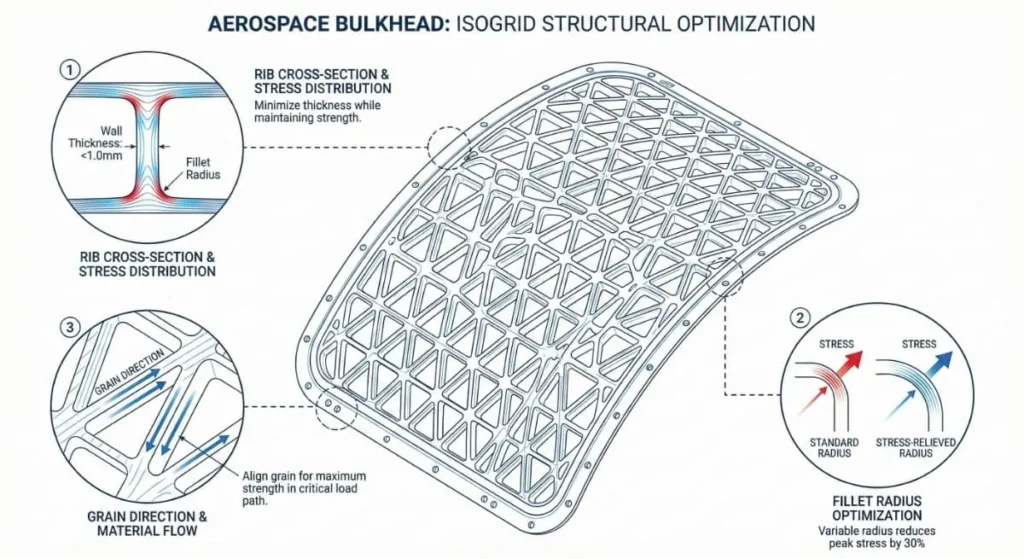
Note: In this industry, a manufacturer is only as good as their measurement equipment. If a shop cannot verify the tolerance, they cannot guarantee the part.
Key Applications of Aerospace CNC Machined Parts
We see CNC technology deployed across various aircraft systems. Common components include:
- Engine Components: Turbine blades, housings, and manifolds.
- Landing Gear: Main struts, wheels, and brake components.
- Interior Structures: Seat frames, overhead bins, and latch mechanisms.
- Fuselage Parts: Wing ribs, spars, and structural brackets.
4. Materials Matter: Machining Exotic Alloys
A significant portion of the cost and complexity in producing aerospace cnc machined parts comes from the materials. Aerospace engineers select materials based on their strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance. However, the very properties that make these materials excellent for flying make them notoriously difficult to machine.
Aluminum Alloys (The Lightweight Workhorse)
Aluminum is the backbone of the aerospace industry due to its low density and high corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum 7075 (T6/T651): Known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, comparable to some steels. It is often used for highly stressed structural cnc machining aerospace parts.
- Aluminum 6061: More workable and corrosion-resistant, often used for internal fittings and less critical structural components.
Titanium (The Heat Resistant Giant)
Titanium is favored for engine parts and fasteners due to its ability to withstand extreme heat and corrosion.
- Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5): The most common titanium alloy.
- Machining Challenge: Titanium has low thermal conductivity. Heat generated during cutting doesn’t dissipate into the chip; it stays in the tool. This requires precision aerospace cnc machining parts manufacturers to use specialized coolant strategies and lower cutting speeds to prevent work hardening.
Inconel and Superalloys
Used in the hottest sections of jet engines (combustors and turbines).
- Inconel 718: A nickel-chromium-based superalloy.
- Machining Challenge: Extremely hard and abrasive. It requires high-performance carbide or ceramic tooling and rigid machine setups to avoid tool breakage.
Engineering Plastics
- PEEK & Ultem: Used for electrical insulators, bushings, and interior components where fire, smoke, and toxicity (FST) standards must be met.
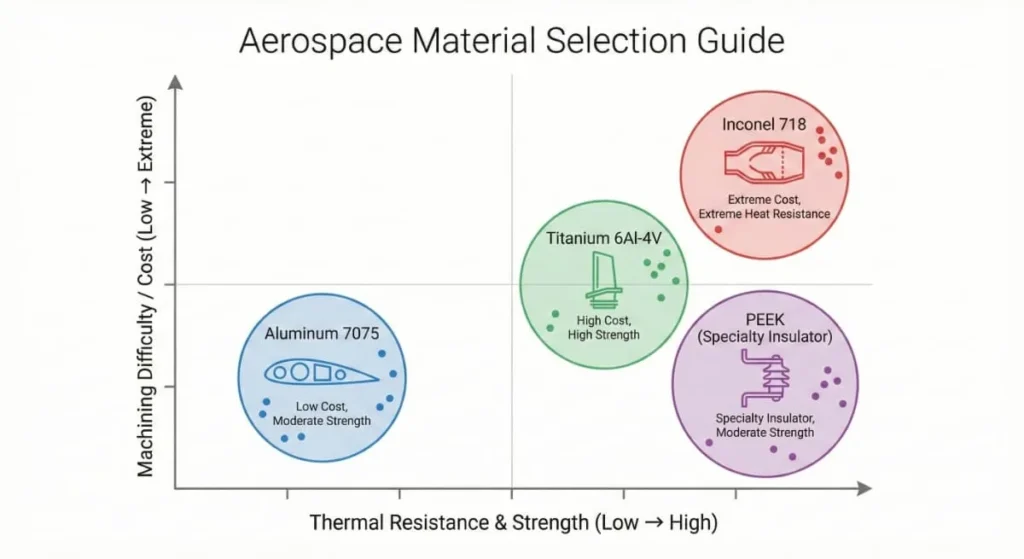
Material Comparison Table:
| Material | Strength | Heat Resistance | Machinability | Typical Application |
| Aluminum 7075 | High | Low | Good | Wing structures, gears |
| Titanium Gr 5 | Very High | High | Poor | Jet engine parts, fasteners |
| Inconel 718 | Extremely High | Very High | Very Poor | Turbine blades, exhaust |
| PEEK | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Cable insulation, connectors |
5. The Manufacturing Process: From CAD to Flight
To produce cnc machined parts for aerospace, a factory must utilize advanced technology. Standard 3-axis milling is often insufficient for the complex geometries required by modern aviation.
The Necessity of 5-Axis CNC Machining
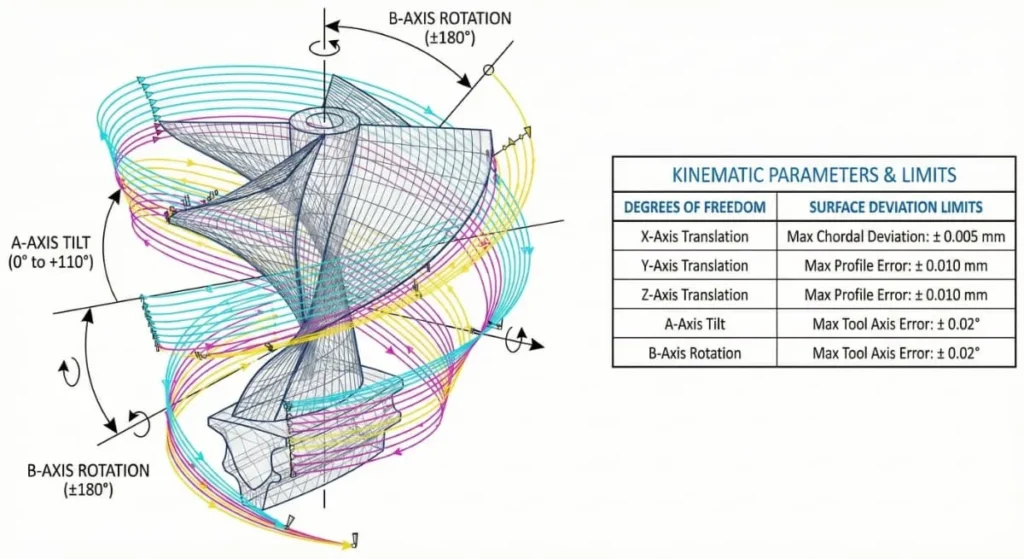
5-axis machining allows the tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction. The cutting tool moves across the X, Y, and Z linear axes while also rotating on the A and B axes.
Benefits for Aerospace:
- Complex Shapes: Essential for airfoils, impellers, and turbine blades.
- Single Setup: CNC machining aerospace parts can be machined in a single setup, reducing the “stack-up error” that occurs when manually flipping parts between operations.
- Tool Access: Allows shorter cutting tools to be used, reducing tool vibration and improving surface finish.
CNC Turning for Shafts and Cylinders
For cylindrical cnc machining aerospace parts like landing gear struts or hydraulic valves, CNC turning centers with live tooling are utilized. This allows for turning, drilling, and milling to happen on the same machine, ensuring concentricity and perfect alignment of features.
6. Visualizing the Process (Image Prompts)
To help you understand our production environment, here are descriptions of the visual standards we maintain.
Image Suggestion 1:
- Prompt: A close-up, high-resolution photo of a 5-axis CNC machine cutting a complex titanium turbine blade. Cool blue lighting, metallic shavings visible, coolant spraying. The focus is on the interaction between the carbide tool and the metal.
- Alt Text: 5-axis cnc machining aerospace parts using titanium alloy for turbine components.
Image Suggestion 2:
- Prompt: A professional quality control engineer in a clean room environment using a CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) probe to inspect a shiny aluminum aerospace bracket. Digital screen in background showing 3D CAD data.
- Alt Text: Quality inspection of aerospace cnc machined parts using CMM for tight tolerances.
Image Suggestion 3:
- Prompt: A flat lay arrangement of various finished aerospace components (gears, manifolds, brackets) on a clean manufacturing table, showing different surface finishes like anodizing and passivation.
- Alt Text: Assortment of cnc machined parts for aerospace with various surface finishes.
7. Surface Finishing: More Than Just Aesthetics
In aerospace, surface finishing is functional, not just cosmetic. It protects cnc machining aerospace parts from the harsh environment of high altitude and saline atmospheres.

- Anodizing (Type II & Type III): Increases corrosion resistance and surface hardness for aluminum cnc machining aerospace parts. Hard anodizing (Type III) is crucial for wear resistance.
- Passivation: Essential for stainless steel and titanium. It removes free iron from the surface, enhancing the natural corrosion-resistant oxide layer.
- Bead Blasting: Used to create a uniform matte finish and remove machining marks, often prepared before anodizing to ensure better adhesion.
- Chemical Film (Chromate Conversion): Conductive coating that provides corrosion protection while maintaining electrical conductivity (crucial for grounding).
8. Quality Assurance: The Backbone of Aerospace Manufacturing
When searching for precision aerospace cnc machining parts manufacturers, their Quality Management System (QMS) is the first thing you should verify.
AS9100 vs. ISO 9001
While ISO 9001 is a general quality standard, AS9100 is the aerospace-specific extension. It adds strict requirements regarding:
- Risk Management: Identifying potential failures before production begins.
- Counterfeit Part Prevention: Ensuring raw materials are genuine.
- Configuration Management: Ensuring the revision of the part being made matches the customer’s drawing exactly.
Inspection Protocols
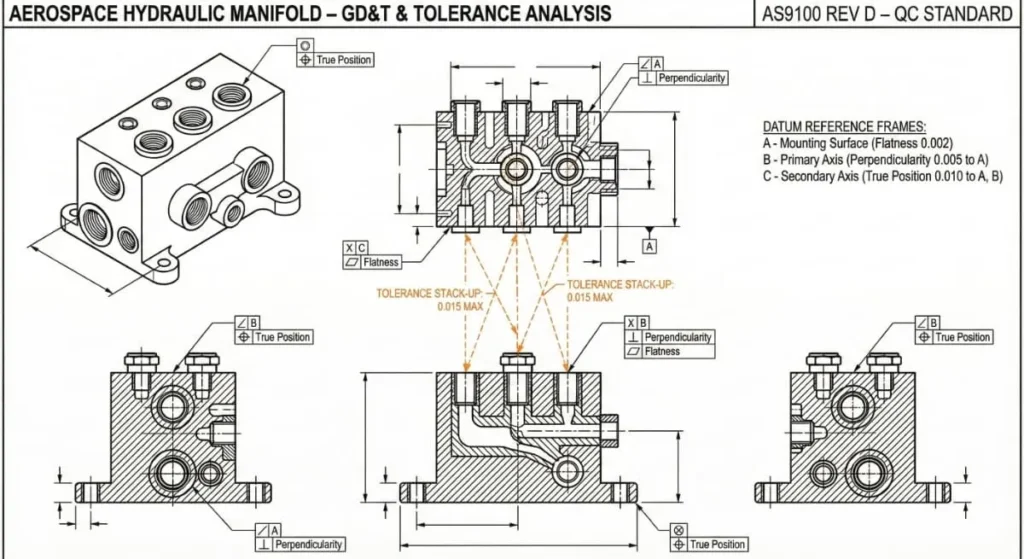
Reliable manufacturers employ a multi-layered inspection process:
- IQC (Incoming Quality Control): Verifying raw material composition using OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry).
- IPQC (In-Process Quality Control): Operators check parts during machining to catch drift immediately.
- FQC (Final Quality Control): 100% inspection of critical dimensions using CMM and geometric tolerancing (GD&T) verification.
Expert Insight: Always request a First Article Inspection (FAI) report (often AS9102 format) before full production. This validates that the manufacturing process can consistently produce cnc machining aerospace parts that meet engineering drawings.
9. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Tips for Aerospace Engineers
To reduce costs and lead times without sacrificing quality, consider these DFM tips when designing aerospace parts cnc machining manufacturing workflows:
- Standardize Radii: Avoid specifying corner radii that require custom tools. Stick to standard cutter sizes.
- Limit Tight Tolerances: Only apply tight tolerances (e.g., +/- 0.005mm) to mating surfaces. Applying them to the whole part skyrockets costs unnecessarily.
- Wall Thickness: Avoid extremely thin walls in aluminum (under 0.5mm) as they vibrate during machining, leading to chatter and poor surface finish.
- Text & Lettering: If part numbers must be machined, choose recessed text rather than raised text to save machining time.
10. How to Choose the Right Manufacturer
Sourcing cnc machined parts for aerospace from overseas offers significant cost advantages, but due diligence is required. Here is a checklist for Procurement Managers:
- Material Traceability: Can they provide Mill Test Certificates (MTC) for every batch of metal?
- Equipment List: Do they have genuine 5-axis machines (e.g., Mazak, DMG Mori, or high-end equivalent)?
- Inspection Reports: Do they offer full dimensional reports with every shipment?
- English Communication: Can their engineering team discuss GD&T and DFM feedback clearly in English?
We pride ourselves on ticking every box on this list. Our facility is equipped to handle the complexities of cnc machining aerospace parts with the professionalism you expect from a top-tier supplier.
11. FAQ: Common Questions About Aerospace Machining
Q: What is the typical lead time for cnc machining aerospace parts?
A: Lead times vary based on complexity and finishing. Typically, simple cnc machining aerospace parts take 2-3 weeks, while complex 5-axis cnc machining aerospace parts with special coatings may take 4-6 weeks. We offer expedited services for AOG (Aircraft on Ground) situations.
Q: Can you handle low-volume, high-mix orders?
A: Yes. Unlike automotive manufacturing which relies on mass production, aerospace parts cnc machining manufacturing is often low-volume (1-100 units). We specialize in high-mix, low-volume production.
Q: Do you machine exotic alloys like Inconel and Hastelloy?
A: Absolutely. We have the tooling and expertise to machine superalloys used in high-heat engine environments.
Q: How do you ensure intellectual property (IP) protection?
A: We sign comprehensive NDAs (Non-Disclosure Agreements) with all clients. Your drawings and proprietary designs are stored on secure servers with restricted access.
12. Conclusion
The production of cnc machining aerospace parts is a discipline that marries engineering creativity with rigorous scientific control. It requires a deep understanding of material properties, advanced multi-axis machinery, and a quality culture that refuses to cut corners.
Whether you are in the prototype phase or looking to scale production for a fleet, the partner you choose will determine the success of your supply chain. You need a manufacturer that offers transparency, precision, and reliable delivery.
Ready to elevate your manufacturing?
Don’t let supply chain uncertainty ground your projects. Partner with a team that understands the gravity of aerospace requirements.
Upload your drawings for a free DFM review and Quote today – Our engineers will analyze your files for manufacturability and provide a comprehensive cost breakdown within 24 hours.
References:
- ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems Requirements
- AS9100 Rev D – Quality Management Systems – Requirements for Aviation, Space and Defense Organizations
- MMPDS (Metallic Materials Properties Development and Standardization)

