Brass CNC Machining: C360 vs H62 vs H65 Selection Guide
By The CNMP Expert Team
Brass is the “Speed King” of the manufacturing world. With a machinability rating of 100%, it sets the benchmark for efficiency.
However, “Brass” is a vague term. In the global supply chain, a simple request for “Brass” can lead to a disaster. A part designed for the American C360 standard might be manufactured using Chinese H62, leading to different mechanical properties and brass cnc machining behaviors.
At CNMP, we bridge the gap between international standards. Whether your drawing specifies ASTM, JIS, or GB grades, we know how they behave under the cutter.
In this comprehensive guide, we extend beyond the basics to analyze the 6 Major Families of alloys used in brass cnc machining, helping you navigate the trade-offs between speed, strength, ductility, and compliance.
1. The “Free-Cutting” Family (C360 / H59 / C385)
The Industry Standard. Maximum Speed.
This is the default choice for 90% of screw machine parts.
C36000 (Free-Cutting Brass) / HPb59-1
- The Equivalents: US: C36000 | China: HPb59-1 | EU: CuZn39Pb3
- The Science: High Zinc (~37%) + High Lead (~3%). The lead acts as a lubricant and breaks chips instantly.
- The Machinist: “Rating: 5/5. The Dream.””In brass cnc machining, this alloy creates fine, dust-like chips. We can drill deep holes without pecking. It offers the best surface finish and the lowest tool wear of any metal.”
- Best For: Standoffs, nuts, bolts, complex fittings.
C38500 (Architectural Bronze)
- The Application: similar to C360 but optimized for Extrusions (Bars and Profiles).
- The Machinist: “Cuts just as fast as C360. Used when the raw material comes in a specific shape (like a hex bar or L-shape) to reduce machining time.”
2. The “Structural & Marine” Family (H62 / C28000 / C464)
Stronger, Cheaper, Tougher.
When you need brass that is stronger than standard C360 or needs to survive in the ocean.
H62 (China) / C28000 (Muntz Metal)
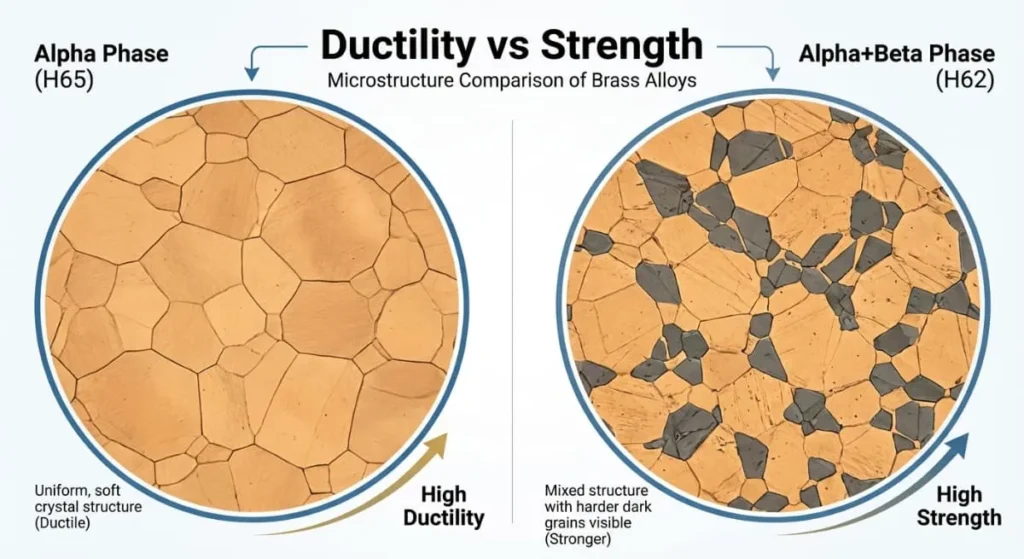
- The Science: ~62% Copper. It is a “Two-Phase” (Alpha+Beta) brass. The Beta phase makes it harder and stronger than C360.
- The Machinist: “Rating: 3.5/5. Crunchy.””H62 is a workhorse in Asian manufacturing. It is harder than C360 and produces short, curled chips. It is cheaper than C360 (less processing). If your part doesn’t have tiny micro-holes, H62 is a great cost-saving alternative for brass cnc machining.”
- Best For: Valve bodies, fasteners, hot-forged parts.
C46400 (Naval Brass)
- The Science: Copper + Zinc + Tin (Sn).
- The Expert: “The Tin adds massive corrosion resistance against seawater. It prevents ‘Dezincification’ (where salt water eats the zinc out of the brass).”
- Best For: Marine hardware, propeller shafts, underwater fittings.
3. The “Cold Forming” Family (H65 / H68 / C260)
Ductile, Bendable, Gummy.
These alloys are designed to be bent, riveted, or crimped after machining.
H65 (C27000) & H68 (C26200)
- The Science: Higher Copper content (65-68%). This creates a “Single Phase” (Alpha) structure, which makes the metal soft and ductile.
- The Machinist: “Rating: 2.5/5. Stringy Nightmare.””Be careful specifying these for brass cnc machining. They act like pure copper. They produce long, continuous ribbons (bird nests) that wrap around the tool. Drilling is difficult. Use these ONLY if you need to bend the part cold.”
C26000 (Cartridge Brass)
- The Application: The most ductile brass. Used for making bullet casings (deep drawing).
- Machinability: Poor (Rated 30%). Very gummy. Avoid for pure milling parts.
The “Lead-Free” Family (Eco Brass / C693)
Regulatory Compliance (RoHS / REACH).
Lead is being banned in drinking water and medical devices. You need alternatives.
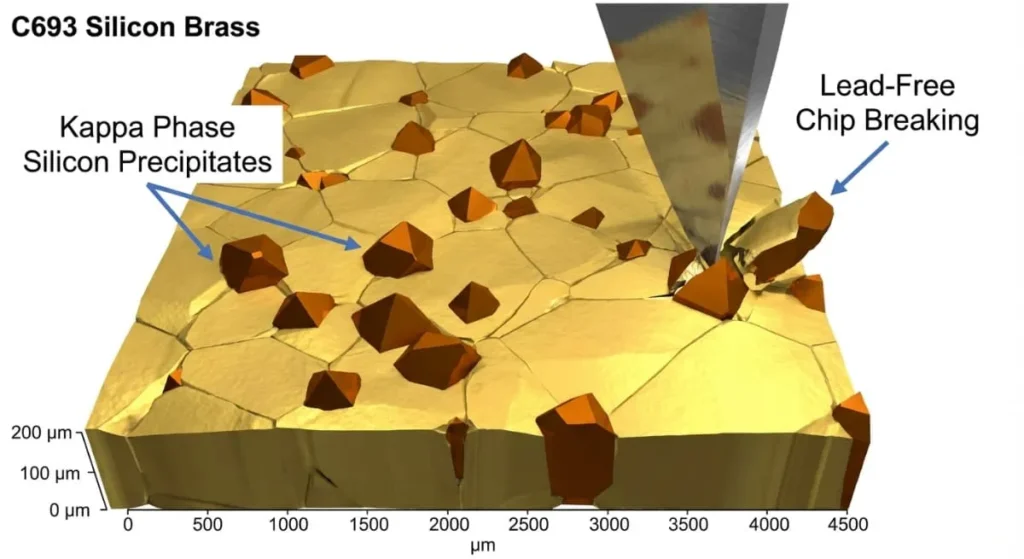
C69300 (Silicon Brass / Eco Brass)
- The Science: Uses Silicon instead of Lead to break chips.
- The Machinist: “Rating: 4/5. Hard but Manageable.””This is the future of brass cnc machining. It creates short chips like C360, but it is much harder (tougher on tools). It is stronger than Stainless Steel 304 in some cases! Expensive, but compliant.”

Global Equivalent & Application Matrix
This chart is your quick reference for sourcing materials from China vs. the West.
| US Grade (ASTM) | China Grade (GB) | ISO / EU | Machinability | Strength | Ductility | Best For |
| C36000 | HPb59-1 | CuZn39Pb3 | 100% (Best) | Med | Poor | High Speed Turning, Screws |
| C28000 | H62 | CuZn40 | 70% (Good) | High | Fair | Valves, Structural Bolts |
| C27000 | H65 | CuZn35 | 40% (Gummy) | Med | High | Springs, Rivets, Wire |
| C26000 | H68 / H70 | CuZn30 | 30% (Poor) | Med | V. High | Deep Drawn Parts, Casings |
| C46400 | HSn62-1 | CuZn38Sn1 | 60% (Fair) | High | Fair | Marine, Saltwater |
| C69300 | — | — | 80% (Hard) | V. High | Fair | RoHS / Lead-Free Parts |
Expert Advice: How to Specify for Brass CNC Machining
1. Don’t Just Say “Brass”.
If you send a drawing to a Chinese factory saying only “Material: Brass”, they will likely use H62 or H59 (Recycled) because it’s cheaper.
- The Risk: If you need high-speed drilling, H62 might break small drills.
- The Fix: Specify “C36000 or Equivalent HPb59-1” for precision turned parts.
2. The Cost of Copper Content.
H68 (68% Copper) is significantly more expensive than H59 (59% Copper).
- Rule of Thumb: Lower Copper = Cheaper + Better Machinability. Higher Copper = More Expensive + More Ductile. Only pay for the copper you need.
3. Cosmetic Considerations.
- C360/H59: Pale Yellow / Gold.
- H65/C260: Rich, Deep Yellow (looks more like gold).
- C464: Slightly reddish tint due to Tin.
Ready to start?
At CNMP, we stock all major grades of brass. Contact Us to discuss which grade offers the best balance of cost and performance for your brass cnc machining project.

